Performance Data Collection - HUR Journaling Issues
Objective
- How to collect performance data when there is an issue with Hitachi Universal Replicator (HUR) journaling
Environment
- Universal Storage Platform V (USP V), RAID600
- Universal Storage Platform VM (USP VM), RAID600
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP), RAID700
- Hitachi Unified Storage VM (HUS VM), HM700
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP G1000), RAID800
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP G5x00), RAID900
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP Gx00), HM800
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP Gxx0), HM850
- Virtual Storage Platform (VSP) E Series
Procedure
HUR is a pull technology and journaling performance is dependent on a many parts such as:
- Primary Storage resource performance (MCU)
- Remote Secondary Storage resource performance (RCU)
- Replication link performance (for example Network connections, Fabric ISL, WAN, Telecoms)
- Local replication targets with delta such as TrueCopy (TC) or Global Active Device (GAD) storage
- Note some configurations do not include a Local or HUR delta system or link
Below is an example of a GAD 3DC HUR solution:
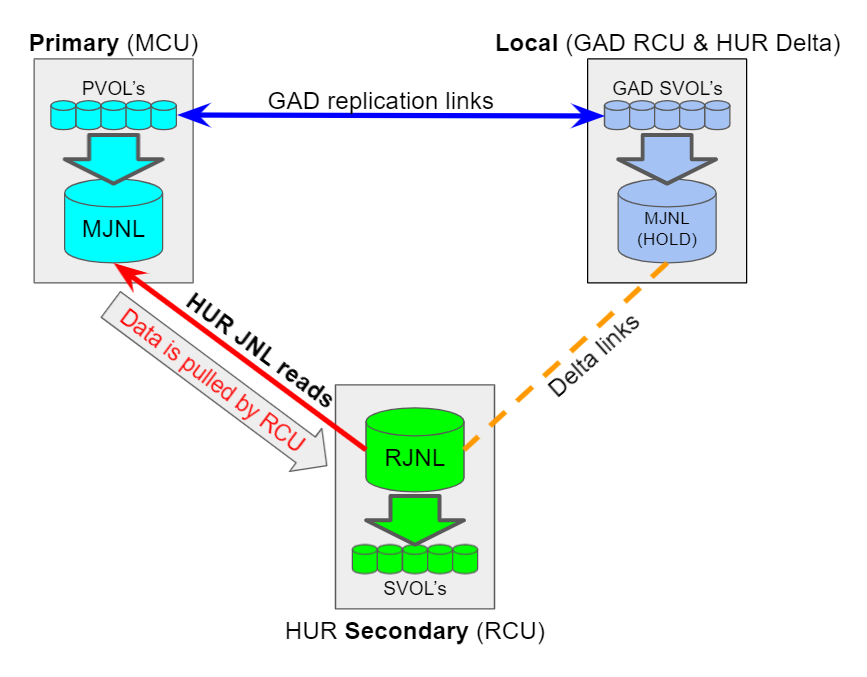
It is critical for any Journal diagnosis and investigation that we receive the receive full solution details and coordinated data from all parts as follows:
- Please ensure monitoring is enabled at 1-minute intervals and all active Control Units (CU) have been enabled for monitoring on all Storage systems, in particular the Journal Volume CU must be enabled:
- Note that detailed performance data is only stored for up to 24 hours so data collection may need careful timing to capture an issue (for example capturing a period of journal growth)
- There is no reason to provide any data which does not capture a problem or event as we will be unable to progress any investigation
- On busy systems logs will wrap quickly so please collect data as soon as possible or within 24 hours after an incident
- Start mode31 or detailed dumps on all Storage Systems:
- Automatic method: Enterprise - How to Collect a Dump Using Remote Ops SVP Agent Version C6 or Higher
- Manual method: Enterprise Data Collection
- Collect performance export data from all Storage systems, RCU, MCU and optional Local Delta (if it is used):
- If RPO is rising to unacceptable levels we will require RPO reports for the same period as the performance data.
- Note: we cannot extract RPO from performance or dump data so your script and calculations need to be supplied.
- Hitachi Protection Manager (part of Ops Centre) can provide RPO reporting
- While the data collections complete please add the following information to the case to assist with investigations:
- Provide details of the issue and the business or application impact
- Provide a by minute timeline of the issues: first & last occurrence, start/end time of captured problem
- Identify which Master Journal (MJNL) and/or Remote Journal (RJNL) are having issues
- Provide an overall design of the MCU, RCU, Local Storage connectivity and any cascaded replication
- Provide distances and details of replication links including: distances of each link, bandwidth, protocols and equipment used
- Provide details and schedules of any related "in-system replication" operations using the HUR Primary Volumes (PVOLs) or Secondary Volumes (SVOLs)
Additional Notes
HUR is a pull technology:
- PVOL write data is packaged up and stored in the Master MJNL which could be in cache or even destaged to JNL-Vol.
- The Remote RCU Storage Initiator ports will pull data from the Primary MCU Storage target ports.
- In some models the replication ports may be universal ports capable of both initiator and target roles.
- The pulling process is know as "journal read" because the RCU reads data from the MCU.
- The RJNL will make "journal reads" to the Master Journal MJNL and then the RJNL will "restore" data to the target SVOLs.
- Note that depending on resources part of the MJNL/RJNL may be in cache or on disk in Journal Volumes (JNL-Vols).
Training Videos are available on the Hitachi Vantara YouTube channel:
In-system replication can be a performance factor in a HUR solution especially when used with the UR PVOLs or SVOLs. In-system replication types are:
- Shadow Image (SI)
- Thin Image (TI)
- Snapshot (COW)
- Flash Copy (FC)
